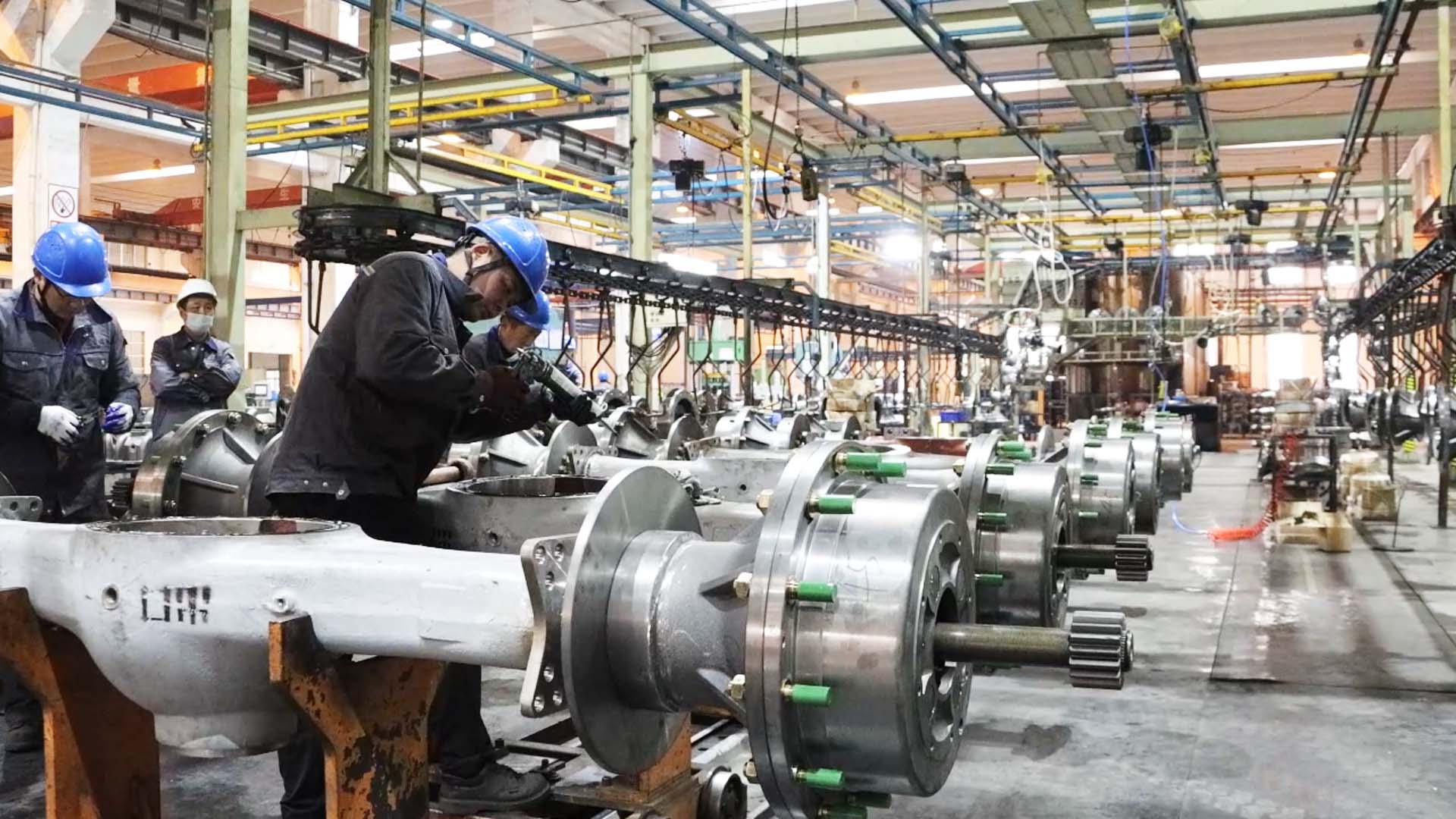
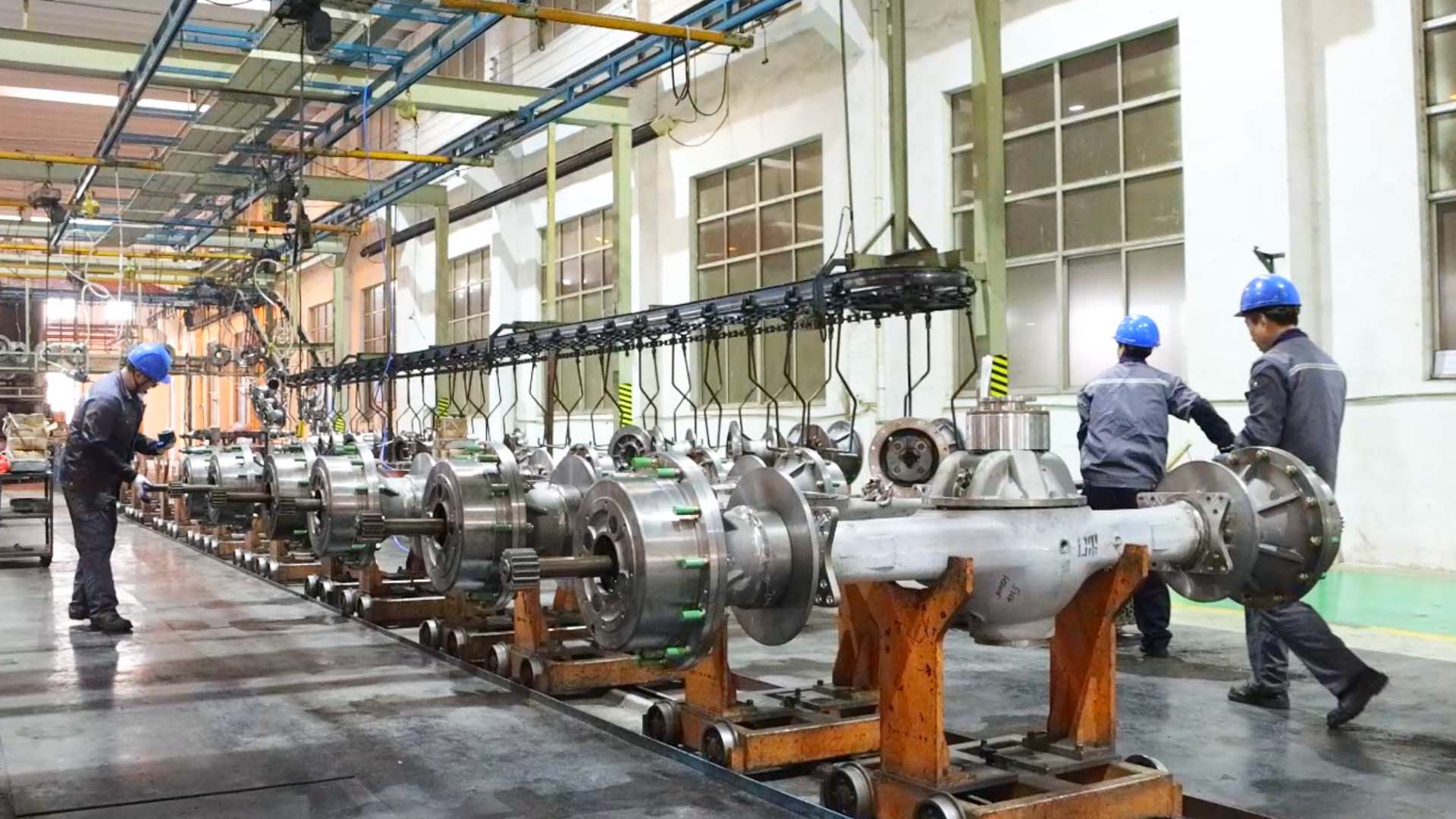
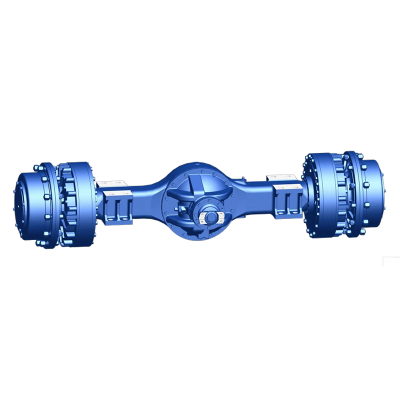
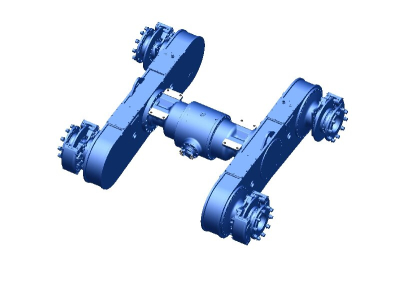
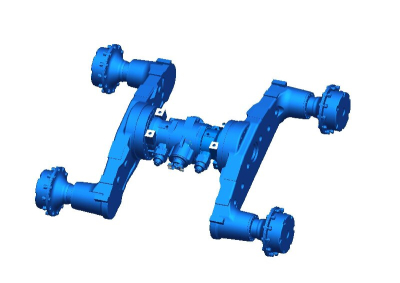
Structure of the leading bridge
The main axle consists of the main gear, differential, axle shafts, and axle housing.Its functions are as follows:
① Transmit engine torque from the universal transmission device to the drive wheels via the main transmission, differential, axle shaft, etc., ensuring speed reduction and torque increase;
② Change the direction of torque transmission using the main gear cone pair;
③ Ensure different angular rotation of the inner and outer wheels during turns using a differential.
Steering drives are also equipped with equal angular velocity joints (CV joints).In addition, the drive axle must perceive vertical, longitudinal, transverse forces and reaction forces between the road surface and the frame or body of the vehicle.
1.Main transmission
The purpose of the main gear is to increase the torque output and accordingly reduce the rotation speed, as well as change the direction of torque rotation when installing the motor longitudinally.There are many types of main transmissions: single-stage, two-stage, two-speed, with gearboxes, and others.
1.1 Single-stage main transmission
A device that reduces speed using a single pair of reduction gears is called a single-stage main transmission.Advantages: simple design, small dimensions, low weight, and high efficiency.
1.2 Two-stage main transmission
When engine characteristics and vehicle operating conditions require a high gear ratio of the main transmission, a single-stage bevel gear no longer provides sufficient ground clearance.In such cases, a two-stage main gear with two pairs of gears is used to reduce speed.
1.3 Wheel gearbox
In heavy trucks, SUVs, and large buses where a high gear ratio of the main transmission and increased ground clearance are required, the second stage of the main transmission gearbox is implemented as two identical mechanisms installed next to the drive wheels on both sides.They are called wheel reducers, and the first stage is the main gear.
2.Differential
The differential connects the left and right axles, allowing them to rotate at different angular speeds while transferring torque, which enables the wheels to roll normally.In some multi-axle vehicles, differentials are installed in the gearbox or between axles during direct drive - such differentials are called inter-axle.Their task is to ensure differential action between the front and rear drive wheels during turns and uneven surfaces.
3.Half axis
A driveshaft is a solid shaft that transmits torque from the differential to the wheels, causing them to rotate and propelling the vehicle.Depending on the hub design, the load conditions of the axles vary, so the axles are divided into three types: fully unloaded, semi-loaded, and three-quarter loaded.
3.1 Completely unloaded axle shaft
Fully unloaded structures are usually used in medium and heavy-duty vehicles.The inner end of the axle shaft connects to the differential gear through splines, while the outer end is fitted with a forged flange and secured to the wheel hub with bolts.The hub is supported on the axle housing by two widely spaced tapered bearings.The axle housing is pressed into the rear axle housing, forming the drive axle.With such support, the half-shaft carries only torque without bending loads.Therefore, such a semi-axis is called 'fully unloaded'.
3.2 Semi-unloaded axle shaft
The inner end of the semi-loaded axle is similar to the fully unloaded one and does not perceive bending or twisting loads.However, its outer end rests on the internal part of the axle housing through one bearing, as a result of which the outer end of the axle receives bending moments.Thus, the semi-loaded axle transmits both torque and partially bending forces.This type of construction is mainly used in passenger cars.
3.3 Three-quarter axle shaft
The bending load on the three-quarter axle is between semi-loaded and fully unloaded structures.This type of axle shaft is used rarely, only in some models of passenger cars.
4.Bridge body
4.1 Integrated Bridge Body
Integral bridge housings are widely used due to their high strength and rigidity, as well as ease of installation, adjustment, and maintenance of the main transmission.Depending on the manufacturing method, solid bridge bodies are divided into cast monolithic ones with a central cast part and pressed steel tubes, as well as bodies made from stamped and welded steel sheets.
4.2 Composite Bridge Deck
Composite housings of drive bridges are usually divided into two parts, connected by bolts into a single unit. Such cases are easier to mold and process.